- Ever caught in a loop of never ending thoughts that sound like, “I’ll never get this right,” or “they must secretly hate me”?
- We understand that these thoughts feel real—convincing, even—but what if they’re actually just automatic negative thoughts that are brain glitches?
- It’s often said, “You are what you think.” While there’s some truth to that, it’s also limiting. You are more than the passing thoughts that pass through your mind.
- Yet, if you frequently find yourself trapped in negative thought loops, that phrase can feel like a curse. You might start believing that because you have negative thoughts, you must be a negative person.
- But here’s the thing—most of those distressing, self-critical thoughts? They’re not true. In fact, they might be wildly inaccurate.
- Your brain, like everyone else’s, is susceptible to cognitive distortions—mental traps that warp your perception of reality. These biases make you see the worst in situations, yourself, and others, even when the evidence says otherwise.
- So what are these cognitive distortions, how do these common thinking mistakes affect you, and how can you overcome them?
- We’ll cover all that in this in-depth guide on cognitive distortions, so keep reading.
When anxiety hits, do you know what to do next?
Learn how to calm your body, interrupt fear loops, and regain control step by step.
What are Cognitive Distortions?
- Cognitive distortions are nothing but thinking biases that make you see the world negatively or incorrectly.
- Think of them as mental "traps” that twist reality and lead to unnecessary stress, anxiety, or self-doubt.
- Cognitive distortions may make you think negatively about situations, blame yourself or others, set unrealistic expectations, and more. These distort the way you think and interpret situations, which could harm your mental health.
- The first step toward healing is understanding the problem and you’ve already taken a step in that direction.

Keep reading to learn about these cognitive distortions in detail and take the next steps to overcome them.
14 Common Cognitive Distortions and Ways to Overcome Them
In this section, we’ll discuss some of the most common cognitive distortions and ways in which you can avoid or overcome them. You may not relate to all cognitive distortions, so look for the ones that seem familiar and work on overcoming them.
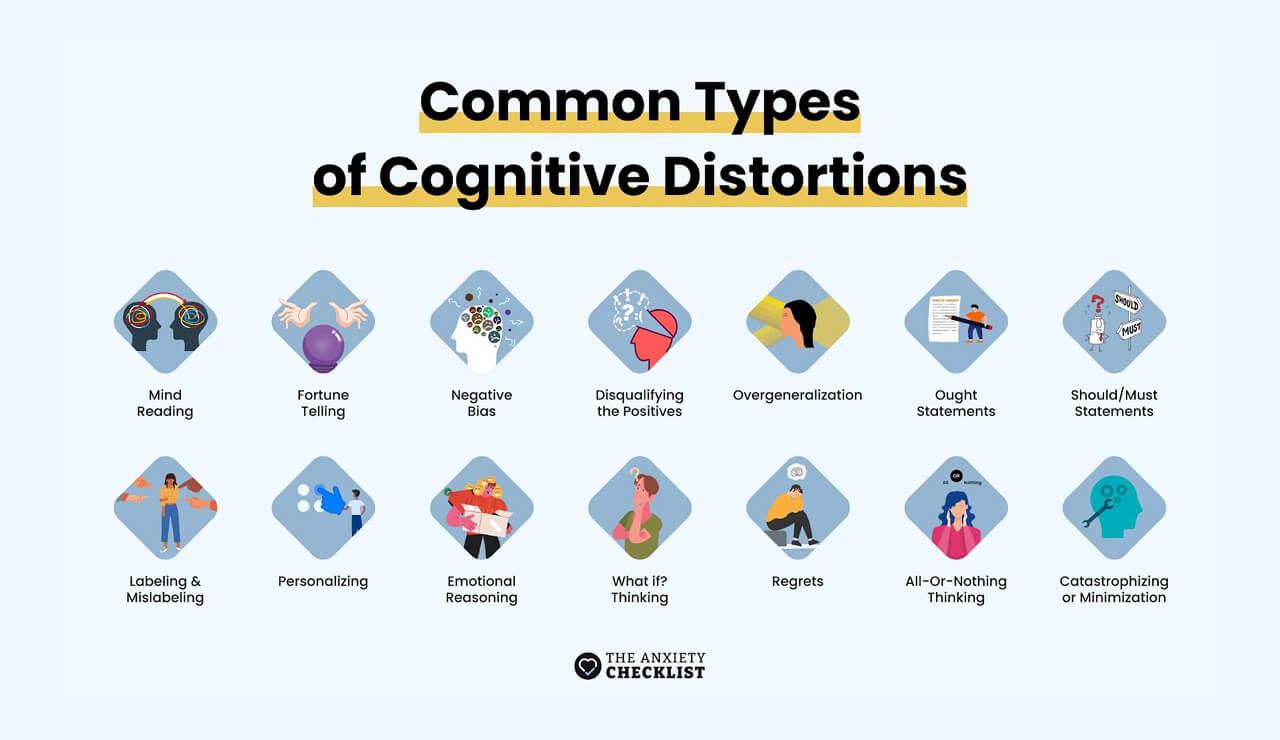
1. Jumping to a Conclusion: Mind Reading 🧠
- Have you ever caught yourself thinking, "They don’t like me or my work," when a colleague barely glances your way?
- Or maybe you’ve assumed a friend’s delayed reply means they’re upset with you—even though there’s no evidence to back that up.
- It happens more often than you think, and you’re not alone. It’s one of the most common cognitive distortions and is called mind reading.
- When these thoughts creep in, remember: you can’t read minds. So, logically, you know that you’re assuming these things without any proof.
- Ask yourself:
- Are there any facts that support this?
- Has the other person said or done anything that can prove your assumption
- Questioning yourself will help you break the loop of automatic negative thoughts (ANT).
- Here are some other tips to help you overcome this common thinking mistake.
- Challenge the Assumption: Remind yourself that you don't actually know what others are thinking.
- Talk It Out: RShare your concerns with a trusted friend or colleague; sometimes a fresh perspective can put things into context.
2. Jumping to a Conclusion: Fortune-Telling 🔮
- Consider the following thoughts:
- "I just know I'll mess up that presentation"
- “I am never going to get promoted”
- Can you relate to these? Have you ever made conclusions that you’re going to fail at things even before trying?
- If the answer is yes, then you, like many others, are facing one of the common cognitive distortions—fortune-telling.
- Sounds ludicrous right? You know you can’t see the future, so how can you be fortune-telling?
- But isn’t that what you’re doing when you’re telling yourself you’re going to fail?
- It’s like having a little voice in your head that always expects the worst, even when things might turn out just fine.
- If you catch yourself making these predictions, try the following tips to clear the fog.
- Ask yourself, "What facts do I have that prove this will happen?" Chances are, you’ll find you have little to no evidence.
- Instead of assuming the worst, consider possible positive outcomes. Challenge these thoughts by reminding yourself that the future is uncertain.
- Focus on the present moment and let go of anxiety about what might happen later.
- It’s one of the cognitive distortions that are common among people who suffer from anxiety disorders or panic disorders. After all, making negative predictions is an outcome of anxious thoughts about the future.
- We recommend you use mindfulness and meditation techniques to reduce anxiety and stop such negative thoughts.
3. Jumping to Conclusions: Emotional Reasoning 🎭
- We’ve all had days where we feel like a failure. But if you assume that to be true based on one or a few bad days, then that’s emotional reasoning.
- Just because you feel it doesn’t make it true.
- See if you relate to any of these:
- You spend most of your day alone and often feel lonely, so you start to believe that you are unloved.
- You get anxious about a presentation and think that you’re not good enough or unprepared.
- These are just examples of emotional reasoning.
- To overcome this cognitive distortion, you need to question these assumptions and ask for proof. Don’t let your emotions guide your beliefs. Challenge your thoughts, look for proof of your assumptions, and then reframe your thoughts.
- For example:
- Distorted Thought: "I feel like a failure, so I must be one."
- Reframed Thought: Feeling like a failure doesn’t mean I am one. Everyone has setbacks, but that doesn’t define me.
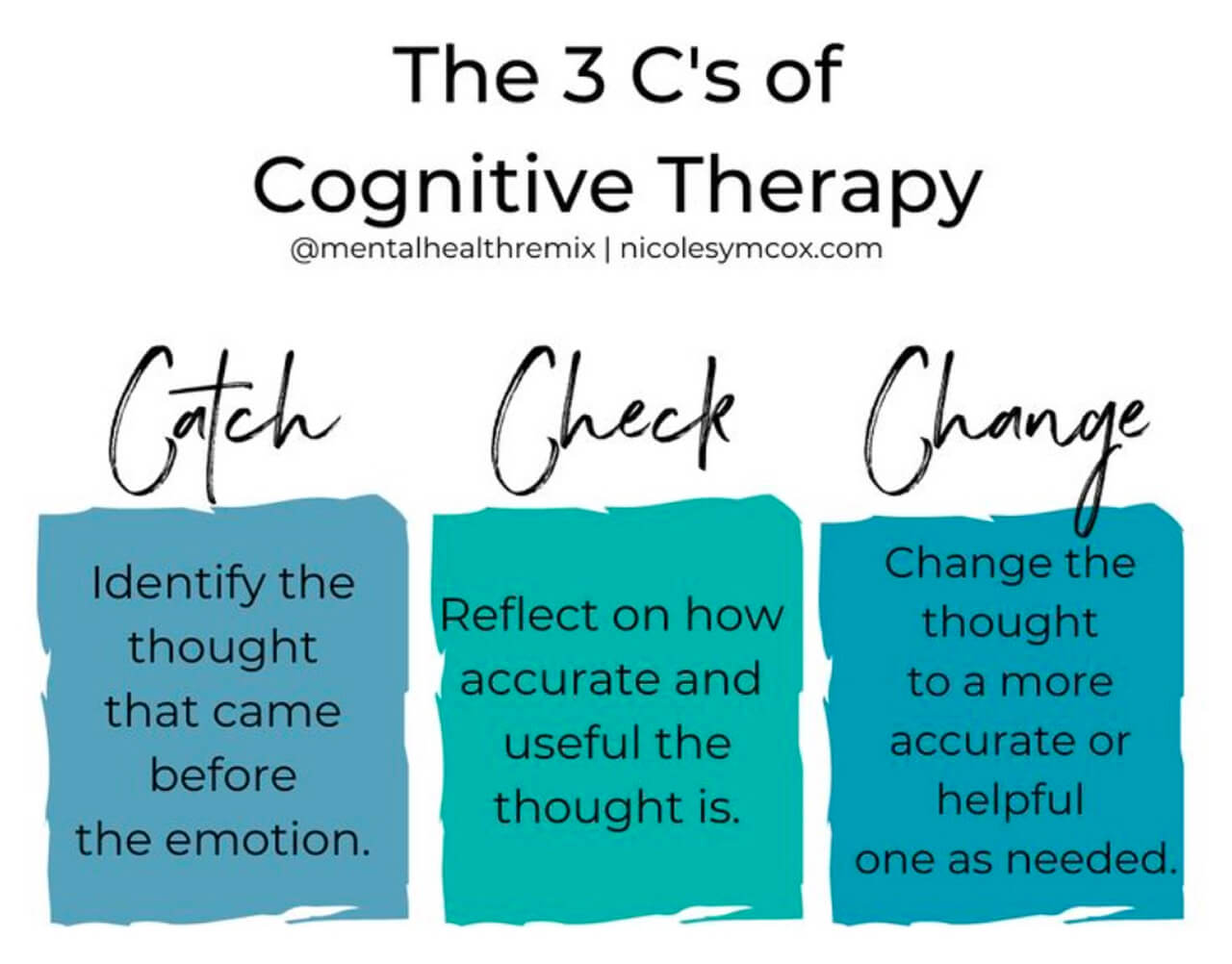
- Follow the 3 Cs of thought reframing used in cognitive behavioral therapy for overcoming cognitive distortions.
4. Negative Filtering: Negativity 👎🏼
- This is a common thinking mistake where you focus on the negative details of a situation. For example, you may receive great feedback on your work but you focus on one negative comment. That’s the negative mental filter at work.
- It’s a common thinking mistake that makes you see the world pessimistically. This can be really saddening and could lower your mood and energy levels.
- If you find yourself always focusing on the negative, you need to consciously stop and question your thoughts.

- You can:
- Shift Your Focus: Consciously remind yourself to notice the positive elements in a situation, not just the negatives.
- Get a Holistic View: Write the good and the bad aspects of a situation, then read both to see the complete picture.
- Practice Gratitude: List three things you appreciate about your day before going to bed. This simple habit can help counterbalance the negativity.
- If you feel overwhelmed and can’t overcome negative thoughts, feel free to cry. There are many benefits of crying, so let yourself go once in a while.
- However, try to get out of these negative overthinking loops caused by cognitive distortions using the tips we’ve mentioned above.
- Here is a short video that can help you learn about the warning signs and strategies for coping with anxiety caused by negative thoughts:
5. Negative Filtering: Disqualifying the Positive 👍🏼
- This is another common thinking mistake, which is very similar to negative thinking. Only in this case, you discount the positive things that happen to you.
- Let us explain.
- Consider these situations:
- You got really good marks on a test, but you tell yourself that you just got lucky.
- Or a client praises your work and you call it a team effort or shrug it off, instead of graciously accepting the compliment.
- This common thinking mistake can lower your self-esteem in the long run. You deserve to accept your wins and be proud of them.
- Try the following tactics to avoid this common thinking mistake.
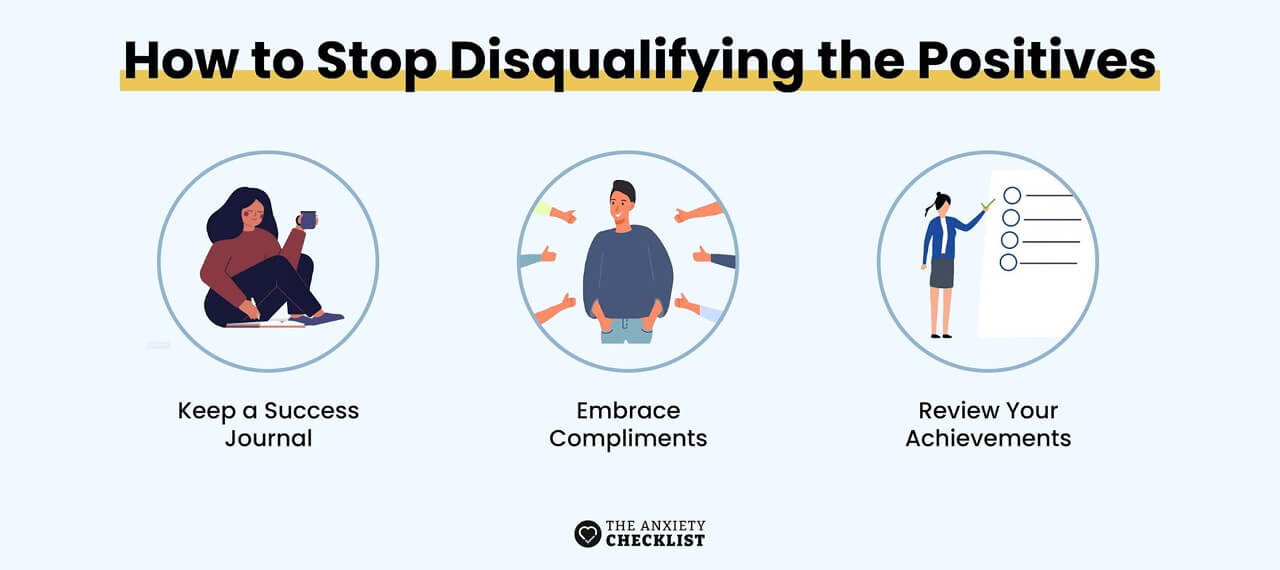
- Keep a success journal to write positive feedback and accomplishments and remind yourself of your strengths.
- Embrace compliments and accept praise without deflecting. Simply say “thank you” and reflect on the positive impact.
- Review your achievements by evaluating completed projects and their positive impact on your business.
6. Negative Filtering: “What if?” Thinking 🙄
- Your mind loves a good what-if spiral, doesn’t it? One little worry turns into a full-blown disaster movie in your head.
- What if I mess up this project? What if they secretly don’t like me? What if something bad happens and I can’t handle it?
- What if, what if, what if…
- Follow these tips to get out of your “what if” thinking loops and avoid such automatic negative thoughts.
- Focus on What’s Real: Are you predicting the future, or is there actual evidence that this will happen?
- Set a Time Limit for Worrying: Give yourself five minutes to spiral and then move on.
- Take Action Where You Can: If your what if has a solution, tackle it. If not, let it go.
7. Unfair Expectations/Blaming: Ought Statements 🤷🏼♂️
- These are statements that you make to either blame yourself or others. These happen because you hold yourself or others to strict, unrealistic standards by saying things like “I ought to do this” or “They ought to have done that.”
- It’s a sure way to set yourself up for disappointment and frustration since no one can meet your unrealistic expectations.
- When you insist that things must be a certain way, you ignore the reality that circumstances vary and mistakes happen.
- Instead of blaming, you need to show grace to both yourself and others. Understand that no one is perfect and everyone makes mistakes.
- To avoid these automatic negative thoughts, try these strategies:
- Challenge Your Standards: Ask yourself if your expectations are realistic or if you’re setting yourself up for failure.
- Communicate Openly: If you feel someone else isn’t meeting expectations, discuss it calmly rather than assigning blame.
- Practice Self-Compassion: Remind yourself that everyone makes mistakes. What’s important is to learn from these mistakes and grow.
- We know it’s difficult to break negative thought patterns, but it’s possible.
8. Unfair Expectations/Blaming: Personalizing 

- Have you ever thought something like "It's my fault they’re upset" or "They didn’t invite me because they don’t like me?”
- That’s personalizing. It means blaming yourself for things that aren’t actually about you.
- It’s like your brain makes you the main character in every negative situation. Does a coworker look stressed? Must be something you did. Did your friend cancel plans? They must be avoiding you.
- In reality, people have struggles that have nothing to do with you, but personalizing makes it feel like it’s all on your shoulders.
- It’s one of the cognitive distortions that make you blame yourself for things that are not in your control.
- Here’s how you can challenge this common thinking mistake.
- Check the Facts: Ask yourself, "Do I have proof that this is about me?" Most of the time, you don’t.
- Consider Other Explanations: Maybe your friend canceled because they’re overwhelmed, not because they dislike you.
- Zoom Out: If this happened to someone else, would you blame them? Probably not, right? So why are you so hard on yourself?
9. Unfair Expectations/Guilt: Should/Must Statements ✨
- Ever catch yourself thinking, “I should be more successful by now” or “I must never make mistakes”?
- Well, these should/must statements are one of the common types of cognitive distortions.
- These may seem like they’re pushing you toward self-improvement, but they’re setting you up for stress, frustration, and failure.
- By making such statements you’re setting strict rules for yourself, and leaving no room for flexibility or compassion.
- To stop yourself from making this common thinking mistake, you can:
- Use gentler, more flexible language. Instead of saying “you must” do something, give yourself room for changes. For example, instead of “I must complete this report tonight” say “I will complete the report as soon as I am able.”
- Understand if there’s an actual deadline or limitations or if you just set those limits for yourself. Whenever you make a should statement, ask yourself “Says who?”
10. Unfair Expectations/Guilt: Regrets 

- Regret has a way of sneaking in and whispering, “You should have done things differently.” It replays old mistakes like a never-ending highlight reel, making you feel stuck in the past.
- Maybe you regret a decision, a missed opportunity, or something you said. And now, your mind tells you that you ruined everything or that things would have been perfect if only you'd made a different choice.
- Sounds familiar?
- Well, it’s a common thinking mistake, so chances are that you would have had regrets at some point in your life.
- While it’s natural to have regrets, it’s not ok to believe that everything is ruined because you made some mistakes.
- You need to:
- Challenge the "perfect past" illusion. There's no way to know if things would have turned out better if you had done things differently.
- Shift from a guilt mindset to a growth mindset. Instead of saying, "I messed up," try "I learned something valuable."
- Focus on what you can control. The past is done, but your next step is entirely up to you.
- You can also consider practicing meditation and breathing exercises to calm your mind and stop any automatic negative thoughts.
11. Rigid, Extreme Thinking: Labeling & Mislabeling 🏷️
- Did you ever make a mistake and thought to yourself “I’m such an idiot.” Or maybe you forgot to call your friend and jump straight to “I’m a bad friend.”
- That my friend is a mind trap or common thinking mistake called labelling.
- If it sounds familiar, don’t worry, it’s one of the common cognitive distortions and you’re not the only one who does this.
- So what is it?
- You’re taking one action and turning it into a permanent identity label.
- Mislabeling takes it one step further as you start doing this to others as well. For example, “They didn’t call me back, they’re selfish.”
- Whenever you see yourself making such judgments based on one action, without context, you need to stop and think.
- People are complex and can’t be defined by such labels.
- Here are some ways in which you can overcome these automatic negative thoughts.

- Separate the Action from the Person: Forgetting something doesn’t make someone irresponsible, it just makes them human.
- Give People and Yourself a Chance: No one is defined by one action. You wouldn’t sum up your best friend’s entire personality based on one bad day, so why do it to yourself?
- Challenge the Label: Ask yourself, “Is this really true 100% of the time?” Have you never been responsible? Has that person never been kind?
12. Rigid, Extreme Thinking: Overgeneralization 🔁
- Overgeneralization happens when you take a single negative event and assume it represents your entire experience.
- For example, if one project doesn’t go as planned, you might conclude that you’re not good at your job. Or, if you forgot to change your baby’s diaper on time in one instance, you think you’re not a good parent.
- There are many such examples. The gist is this: you take one instance and generalize it to make absolute statements.
- This is one of the common cognitive distortions and is bad for your mental health. It could also affect your relationships.
- For example, let’s say your spouse made a mistake. Instead of resolving the problem, you could make it worse by generalizing and saying “You always do this.”
- So how can you avoid this common thinking mistake?
- One of the best ways to overcome overgeneralization is to consciously reframe your thoughts. Here are some examples.
- Distorted Thought: I always mess things up. Reframed Thought: I had a setback this time, but I’ve succeeded on many other occasions.
- Distorted Thought: Nothing ever goes right for me. Reframed Thought: Things didn’t go well for me this time, but I have had many successes before.
- Try to challenge your negative thoughts and reframe them to break this habit of overgeneralizing. It will take time, and sometimes you’ll fail, but still keep trying.
13. Rigid, Extreme Thinking: All-Or-Nothing Thinking 🌓
- Consider the following statements:
- "If I don't get into that school, my life is over"
- “I cheated on my diet, so I might just give up and eat whatever I want”
- “If I don’t get that promotion, I’ll never be successful”
- These are examples of a common thinking mistake called black-and-white thinking or all-or-nothing thinking.
- It’s your mind turning your life into a black-and-white movie when, in reality, there are endless shades of gray.
- If something you want doesn’t happen, it doesn’t mean your life is over. There are never just two outcomes of any situation—best and worst. There are numerous other options in between.
- So, you need to challenge this type of thinking and stop these automatic negative thoughts in their track.
- Here’s how.

- Look for the middle ground. Instead of thinking “I failed,” try “That part was tough, but I handled other things well.”
- Celebrate partial wins. Progress is progress—even if it’s not perfect.
- Notice when you're using extreme words. Always, never, ruined, terrible—those words signal distorted thinking.
14. Rigid, Extreme Thinking: Catastrophizing (Magnification) or Minimization 🤯
- Ever had a small problem that your brain turned into a full-blown disaster?
- "If I mess up this presentation, I’ll lose my job and never recover." Or maybe you’ve downplayed something important? "Yeah, I’ve been feeling awful for weeks, but it’s probably nothing."
- That’s catastrophizing (magnifying the worst-case scenario) or minimization (downplaying things that matter).
- These are two extremes and neither is the likely outcome in any situation. In most cases, things are neither so bad nor so trivial, but somewhere in between.
- By now, you should be able to challenge this common thinking mistake, based on what we’ve discussed earlier. Question the thought, look for proof, and find more realistic alternatives to the extremes.
- Here’s an example of thought reframing.
- Catastrophic Thought: "If I mess up this presentation, I'll lose my job."
- Reframed Thought: "If I make a mistake, I’ll learn from it and do better next time. One error won’t cost me my job."
Frequently Asked Questions
hese are negative or biased thought patterns that distort your thinking. These can make you look at things negatively, inaccurately, or unrealistically.
Mental health conditions like anxiety and depression could cause cognitive distortions and automatic negative thoughts.
The three Cs are: catch it, check it, and change it. These are used for reframing thoughts to avoid cognitive distortions.
Understand that things are never black and white but in multiple shades of grey. Look for a realistic middle ground instead of considering the extreme scenarios.
Challenging your assumptions and reframing your thoughts is the best way to overcome most cognitive distortions.
Ready to Overcome Cognitive Distortions and Stop the Negative Thinking Loop?
- There you have it—some of the most common cognitive distortions that affect people globally.
- If you relate to one or more of these cognitive distortions and want to overcome them, follow the tips we’ve provided for each common thinking mistake.
- Remember, the first step is to understand the bias and challenge your thoughts. Then, with practice, you can learn to reframe them.
- If your automatic negative thoughts and overthinking loops cause you anxiety, we can help. The Anxiety Masterclass offers practical tips and tools to manage anxiety and regain control of your life. You'll have access to exercises designed to rewire your brain and help you lead a happier, more fulfilling life.
Previous Article

Is Overthinking Making Your Anxiety Worse? What To Know
If you are in a crisis or any other person may be in danger - don't use this site. These resources can provide you with immediate help.

Stop guessing. Start understanding your anxiety.
Break free with expert-backed techniques in CBT & Hypnotherapy
- Guided exercises & worksheets
- Mobile app with affirmations, hypnosis & exposure tools
- Clear explanations that actually make sense
- 5+ Hours Anxiety Masterclass (Video)
Top Categories
Related Article
- Overthinking and Anxiety
- Cognitive Distortions
- 5 Emotional Wounds Anxiety
- Love vs Anxiety Relationship
- Generational Trauma Anxiety
- What Happened to You Oprah Winfrey
- Financial Anxiety Relief
- Shadow Work Prompts Anxiety
- Inner Child Healing Steps Anxiety Self Love
- NLP for Anxiety Techniques
- What is Shadow Work
- Fear Ladder Anxiety Tool